Hello everyone!💛
There are different types of cloud environments from which we can select one. But the real question is which is best suitable for your situation? So let's learn about different types of cloud deployment models today so, the next time you choose, you will choose the right one!😉
CONTENTS
- Public Cloud Model
- Private Cloud Model
- Hybrid Cloud Model
- Community Cloud Model
- A Brief of Cloud Service Models
- Deployment and Sevice Models
- Choosing between Cloud Deployment Models
- Cheatsheet
- Examples
Public Cloud Model
This is the most common model of all. Cloud resources like servers, storage are owned and operated by the service provider and are delivered over the internet.
- All the hardware, software and other supporting infrastructure are owned and managed by the cloud provider. No local hardware is required by us to manage.
In a public cloud, several other organisations(cloud tenants) along with you share the same hardware, storage, etc.
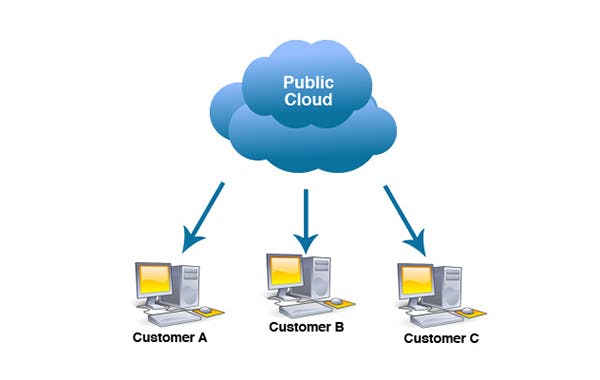
We can access services and manage our account using a web browser.
Advantages
- Highly Scalable: We can scale up or scale down resources as per the organisation's requirement.
- Pay-as-you-go: We will pay only for the resources we use. There is no need to invest in any hardware or software.
- Organisation is not responsible for the maintenance of infrastructure.
- 24/7 uptime The extensive network of your provider’s servers ensures your infrastructure is constantly available and has improved operation time.
Disadvantages
- There may be specific security requirements in some scenarios where public cloud cannot meet.
- Suppose if we have a legacy application, means an application which runs on outdated software, it would be hard for us to maintain using a public cloud.
- Cloud service provider provides only standard service options. Therefore, the public cloud model often fails to satisfy more complex requirements.
Usecases
- If we want to recover our data even if our organisation undergoes some natural disaster then it's best to use public cloud. Since our data is stored by the cloud provider in some other place.
- For an organisation, which constantly undergoes spikes and drops in traffic can choose public cloud because this can save money as the resources can automatically scale up or down with cloud.
- Many companies move their historical data to the cloud to store it for the longer term.
Private Cloud Model
This is also known as the internal or corporate cloud. A private cloud is something which is physically located in your organisation. It can be hosted by a third-party service provider.
- Here we are completely responsible for the purchase and maintenance of hardware and software.
- Private cloud makes it easy for us to customise resources to support any scenario including legacy application.
This cloud model can meet strict security and legal requirements. This means that we have full control over security.
Types of Private Cloud
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): is an on-demand configurable pool of shared computing resources allocated within a public cloud environment, providing a certain level of isolation between the different organizations (denoted as users hereafter) using the resources. (Definition from Wikipedia)
Advantages
- VPC is cheaper than a private cloud.
- A VPC has better security, scalability and flexibility than public cloud.
- Less maintenance than private cloud.
Disadvantages
It is not a private cloud. A VPC is still very restrictive when it comes to customization.
- Hosted Private Cloud: The servers are not shared by other organisations, hosted and maintained only by us.
- Managed Private Cloud: environment is simply a hosted environment in which the provider manages every aspect of the cloud for the organization. This option is appropriate for organizations that do not have the staff that is equipped to manage private cloud environments alone.
Advantages
- High security, privacy and reliability, as only authorized persons can access resources
- We will have the flexibility to customize infrastructure in accordance with our requirements.
Disadvantages
- Expensive than public cloud.
- We have to put some CapEx cost to purchase and maintain the hardware.
- IT department of our organisation will be responsible for the cost and accountability of managing a private cloud.
Usecases
- Private cloud is used when your organisation has a legacy application.
- Private cloud can be used when the public cloud was not able to meet certain security requirements.
Hybrid Cloud Model
Public cloud and private cloud can be combined together to form a hybrid cloud. This allows the data and apps to move between two environments.
- Cloud Bursting: is an application deployment model in which an application runs in a private cloud or data centre and bursts into a public cloud when the demand for computing capacity spikes.
The hybrid cloud model is used when we have some information which we cannot put in a public cloud. For instance, the data which cannot be exposed out can be kept in our organisation's datacentre and we can host our application linking to this data in the public cloud.
Disadvantages
- Hybrid Cloud can be complicated to manage and set-up.
- While creating a hybrid cloud environment, specific hardware is required to deploy on-premises, and that’s what shaves off a large chunk of the budget.
Community Cloud Model
A community cloud model largely resembles the private cloud. The only difference is the set of users. Private cloud is owned only by a single organisation but a community cloud is shared by organisations with a similar background.
Advantages
- A community cloud is cheaper than a private one, yet it offers comparable performance. Multiple companies share the bill, which additionally lowers the cost of these solutions.
Disadvantages
- Every participant in the community has authorized access to the data. Therefore, organizations must make sure they do not share restricted data.
- As this is a community cloud, the systems of one organization may have to adhere to the rules and regulations of other organizations involved in the community as well.
- Limited storage and bandwidth capacity are common problems within community systems.
Usecases
- Organisations which have similar computing concern can together take up community cloud.
A Brief of Cloud Service Models
IaaS
By infrastructure, we mean that cloud service provider provides us with fundamental resources like virtual machines, storage servers, networking and testing environments.
The cloud service provider handles infrastructure whereas consumer/user handles installation, configuration and management of software and applications.
PaaS
Like IaaS, PaaS also provides servers, storage along with software frameworks, middleware, development tools, operating systems and more. As a consumer, we are only responsible for managing hosted applications and services.
PaaS helps us to create an application by managing the underlying infrastructure. It provides a development and deployment environment in the cloud as a cloud provider takes care of underlying infrastructure.
SaaS
In SaaS, everything will be maintained by the cloud provider. SaaS allows users to connect and use cloud-based apps over the internet.
SaaS provides a complete solution which we buy on a pay-as-you-go basis from the provider. Usually, we rent services like CRM(Customer Relationship Management), email, Microsoft Office 365 etc, and connect to these over the internet. All of the underlying infrastructure, middleware, app software and app data are located in the service provider’s data center. Therefore, there will be no pressure for users about app maintenance, infrastructure management as it is not managed by us.
Deployment and Sevice Models
Let's see which service models can be delivered by which deployment models.
| Deployment Models | Service Models |
| Public Cloud Model | PaaS and IaaS |
| Private Cloud Model | IaaS and SaaS |
| Hybrid Cloud Model | PaaS and SaaS |
| Community Cloud Model | IaaS, PaaS and SaaS |
Choosing between Cloud Deployment Models
To choose a model which best suits our requirement we have to consider some factors:
Scalability: Does your application run into sudden demands?
Ease of use: How skilled is your team? How much time and money are you willing to invest in staff training?
Cost: How much resources can you spend on your cloud solution? How much capital can you pay upfront?
Security: Do you want to store any private data that should not be stored in the public cloud?
Privacy: Does this model meet all the privacy requirements?
Flexibility: How flexible are your computing, processing, and storage needs?
Legal compliance : Are there any relevant laws in your country or industry?
Cheatsheet
| Public | Private | Hybrid | Community | |
| Ease of setup | Very easy to set up, the provider does most of the work | Very hard to set up as your team creates the system | Very hard to set up due to interconnected systems | Easy to set up because of community practices |
| Ease of use | Very easy to use | Complex and requires an in-house team | Difficult to use if the system was not set up properly | Relatively easy to use as members help solve problems and establish protocols |
| Data Control | Low, the provider has all control | Very high as you own the system | very high | high |
| Reliability | Prone to failures and outages | High (with the right team) | High (with the right setup) | Depends on the community |
| Scalability | Low, most providers offer limited resources | Very high as there are no other system tenants | High (with the right setup) | Fixed capacity limits scalability |
| Security and Privacy | Very low, not a good fit for sensitive data | Very high, ideal for corporate data | Very high as you keep the data on a private cloud | High (if members collaborate on security policies) |
| Flexibility | no flexibility, service providers usually offer only predefined setups | Very flexible | Very flexible | Little flexibility, setups are usually predefined to an extent |
| Cost | Very Inexpensive | Very expensive | Cheaper than a private model, pricier than a public one | Members share the costs |
| Demand for hardware | No | In-house hardware is not a must but is preferable | In-house hardware is not a must but is preferable | No |
Examples
- Public Cloud Model
- Amazon Web Services
- Microsoft Azure
- IBM Cloud
- Google Cloud Platform
- Private Cloud Model
- VMware
- Dell
- Oracle
- IBM
- Microsoft and
- Amazon Web Services.
- Hybrid Cloud Model
- Microsoft
- VMware
- Amazon Web Services
- Rackspace
- Hewlett-Packard
- IBM
- Cisco and
- Dell
- Community Cloud Model
- NYSE Capital Market Community Platform.
- AWS GovCloud
That's all for today! Hope this helps you and acts as a guide while learning.😍
Disclaimer: Some of the definitions are taken from different resources and are not changed to pass the original definition and meaning to you.
I have done a lot of research to learn this concept. So, to make it easy for my fellow cloud learners I have curated all the important stuff which I learnt and wrote it as an article.
Do let me know in the comments how this article helped you and do let me know if you want me to write on a particular topic.
Drop a like and do share your valuable feedback in comments!
I would love to connect with you through Twitter, LinkedIn, Github.
Articles you may also like
- How to Crack an Interview as a Fresher
- Azure made easy!
- A detailed explanation of Infrastructure as a service(IaaS)
- A detailed explanation of Platform as a service(PaaS)
- A detailed explanation of Software as a service(SaaS)
- REGEX- It's a Piece of Cake!
- Validating Username Using Regex
- Explain to me Like I am Five: Time Complexity
- Do's and Don'ts of Writing a Technical Article!
- Ask Yourself: Why Do I Blog?
- Juggling Algorithm for array rotation
- Markdown Cheatsheet to write a stunning article